The Village Idiot is taking over the Asylym with a little help from The Paypal Mafia and the Teflon Billionaire #Omidyar? #Aadhaar
Palantir, Aladdin Fink, Gates, Musk, Thiel
The video critiques Elon Musk's public persona, debunking myths about his self-made success, highlighting controversies in his businesses like Tesla and SpaceX, and questioning his actions on Twitter and claims of free speech advocacy.
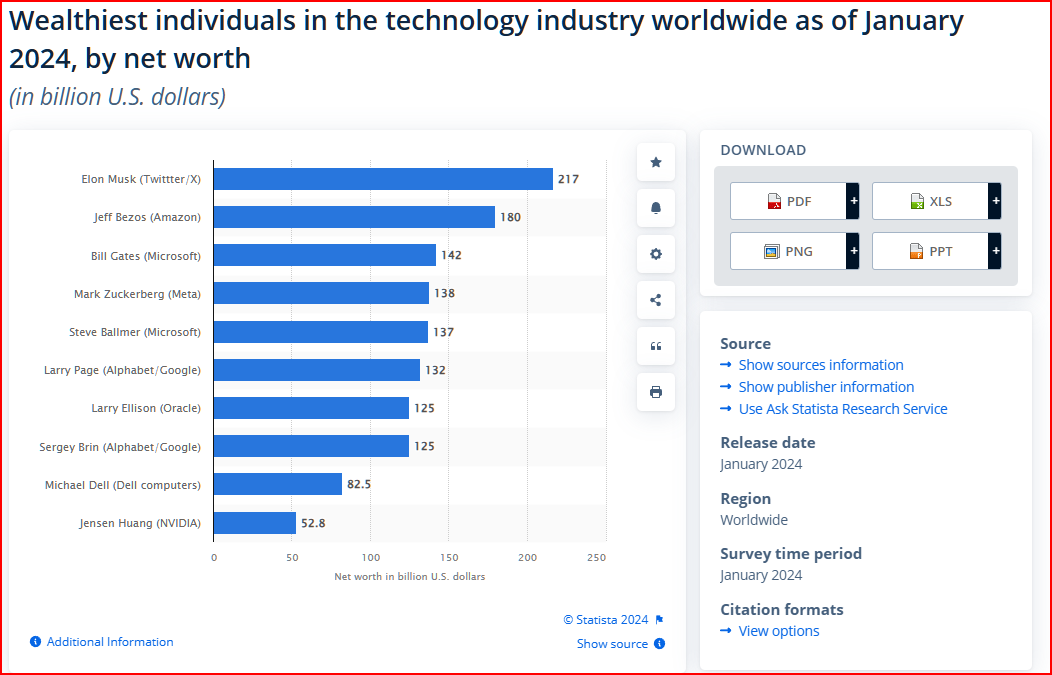
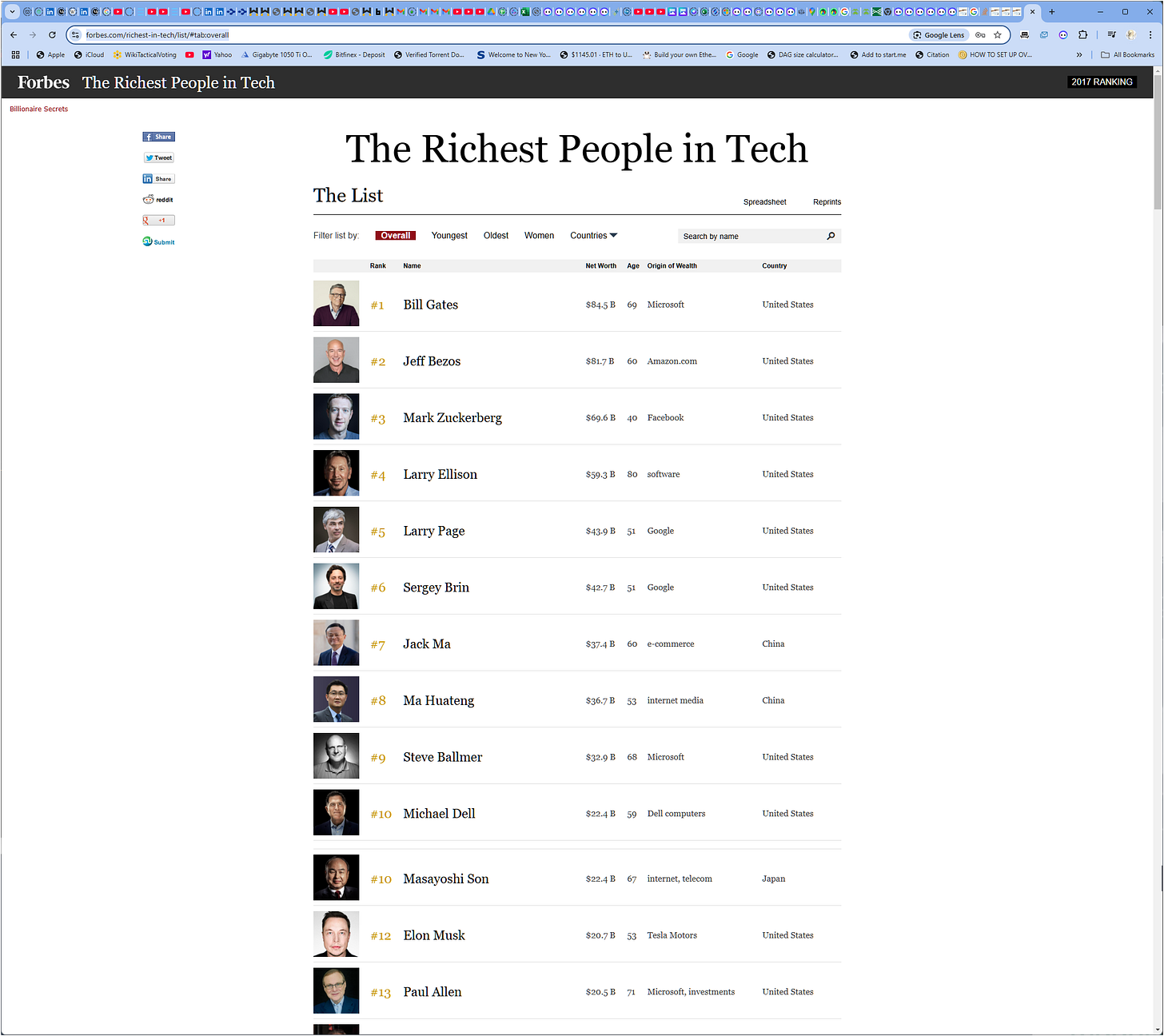
https://www.forbes.com/richest-in-tech/list/#tab:overall
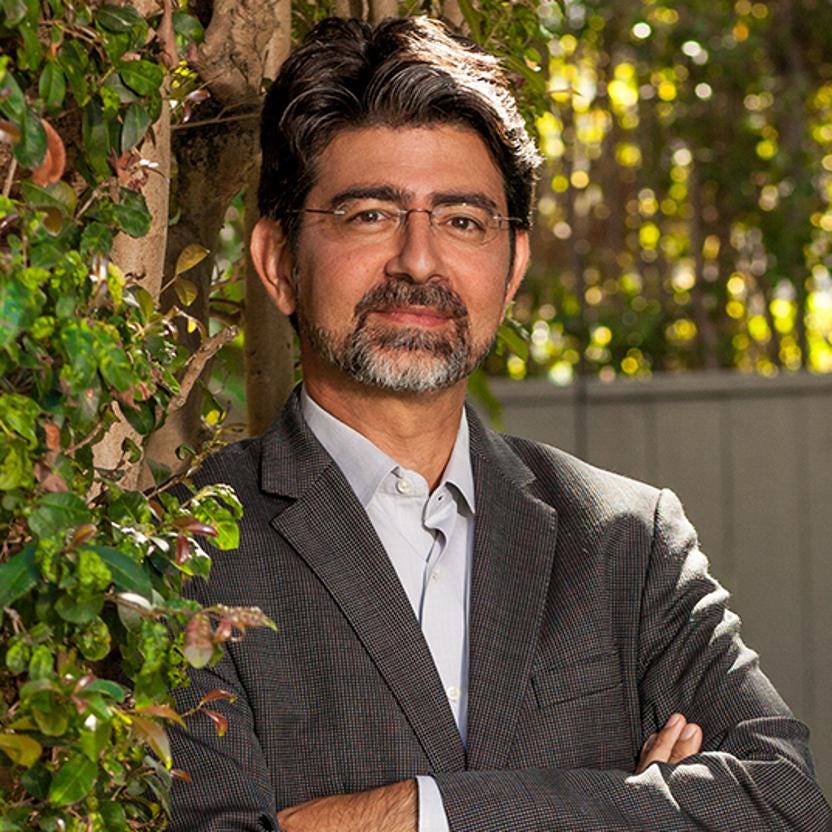
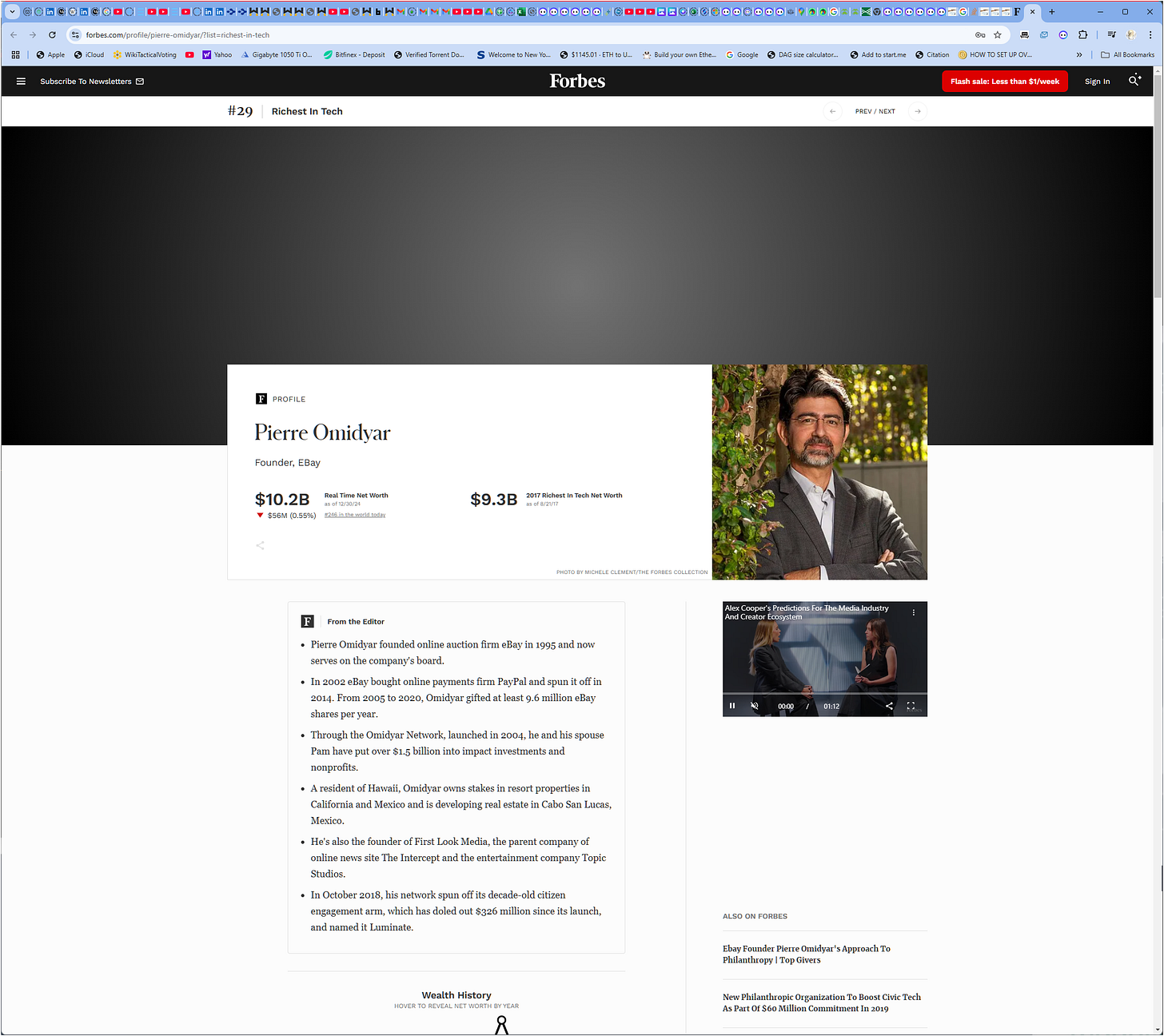
#29Pierre Omidyar$9.3 B57eBayUnited States
https://www.forbes.com/profile/pierre-omidyar/?list=richest-in-tech
The video highlights Omidyar Network's focus on leveraging technology for social impact in India, emphasizing digital identity, inclusivity through mobile internet, and creating opportunities for underserved populations.
Detailed Summary for [Omidyar Network MD shares motive behind Survey "State of Aadhaar: A People’s Perspective"](
by [Monica](https://monica.im)
[00:00](
The video discusses the Omidyar Network's strategic approach to digital identity and its impact on various sectors, emphasizing the importance of technology in enhancing governance and citizen engagement.
- Introduction to the role of digital identity in governance and citizen engagement.}
- Overview of focus areas including property rights, emerging technology, financial inclusion, and education.}
- Insight into the broader customer base of the investees beyond the targeted demographic.}
- Explanation of the 'good tech' investment philosophy which emphasizes technology-led solutions.}
- Introduction to the two components of the 'good tech' approach to investing.}
[01:04](
The video discusses the transformative impact of mobile technology on social inclusivity in India, emphasizing how affordable internet access is enabling underserved populations to access opportunities and realize their potential.
- Introduction of technology's role in driving social good.}
- Mobile technology fosters inclusivity, reaching a broader audience.}
- High mobile phone usage in India, surpassing European data consumption.}
- Low data costs in India facilitate better access for businesses and governments.}
- Opportunities are created for marginalized individuals to achieve their potential.}
Aadhaar, the world's largest biometric ID system, aims to enhance service efficiency in India but faces criticism over privacy concerns, data leaks, and exclusion issues, sparking debates on its implementation and impact.
Detailed Summary for [The Stream - Aadhaar: The world’s largest biometric identification system](
by [Monica](https://monica.im)
[00:08](
The video discusses Aadhaar, India's largest biometric identification system, which aims to provide efficient government services and ensure that all residents have a recognized identity. However, its implementation has faced significant controversy regarding its mandatory nature and concerns over data privacy.
- Introduction to Aadhaar as the world's largest biometric identification system designed to enhance government service efficiency.}
- Aadhaar's goal of inclusivity, aiming to ensure that every Indian resident is part of the identification system.}
- Over 1.15 billion people are enrolled in Aadhaar, allowing access to government services through biometric data.}
- Criticism of Aadhaar for becoming mandatory for certain services, raising concerns about accessibility and privacy.}
- Concerns about the security of Aadhaar's digital infrastructure, with instances of data leaks and technical errors affecting welfare access.}
[03:46](
The discussion revolves around the complexities and implications of the Aadhaar biometric identification system, emphasizing the need for scrutiny and the contradictions between its promises and actual outcomes.
- The speaker reflects on their initial engagement with the Aadhaar project in 2009, highlighting concerns about civil liberties and the necessity of a legal framework.}
- There is a strong emphasis on the importance of questioning and understanding the true nature of the Aadhaar project, rather than accepting it blindly.}
- The speaker critiques the claims made about Aadhaar, noting that its implementation has led to exclusion rather than inclusion, contradicting its stated goals.}
- A conversation unfolds regarding differing opinions on Aadhaar, with one participant expressing dissatisfaction with its performance while another has a positive experience despite the issues.}
- The discussion highlights the challenges of connectivity and digital access in relation to biometric identification, illustrating the broader implications of such technologies.}
[07:34](
The discussion revolves around the challenges and controversies associated with the Aadhaar biometric identification system in India, highlighting reliability issues and the implications for citizens.
- Introduction to the significant issues surrounding the Aadhaar program.}
- A case presented in the Supreme Court raises questions about the reliability of Aadhaar devices.}
- Concerns about the lack of independent data to verify government claims regarding Aadhaar's reliability.}
- A historical perspective on political views about Aadhaar, illustrating a shift in governmental stance.}
- Clarification that many individuals were coerced into enrolling in Aadhaar to access essential services.}
[11:21](
The discussion centers around the Aadhaar system in India, highlighting its dual nature as both a tool for empowerment and a potential cause of exclusion for individuals lacking proper identification.
- A prominent economist criticizes the Aadhaar project, stating that its intended benefits are overshadowed by issues of exclusion.}
- The Aadhaar system is described as creating barriers for individuals who do not receive their identification numbers, leading to loss of access to essential benefits.}
- While acknowledging the exclusion risks, a counterpoint is made about the high percentage of the population that is already enrolled in the system.}
- The speaker suggests that as enrollment increases, the system may soon encompass an even larger majority of the population.}
[15:07](
The discussion focuses on the effectiveness and challenges of the Aadhaar system, emphasizing both its widespread use and the technological advancements that aim to improve its reliability.
- The speaker acknowledges concerns about the reliability of Aadhaar transactions, noting a failure rate of 35-40% in some cases.}
- Aadhaar is described as an open system that allows developers to integrate their services, which can lead to improvements in technology and standards.}
- The speaker draws a parallel between past and present technology, highlighting how advancements in fingerprint recognition are improving the accuracy of Aadhaar transactions.}
- Despite current challenges, the speaker expresses optimism about the future of Aadhaar technology and its potential to reduce failure rates as advancements continue.}
[18:54](
The discussion centers around the legal and privacy implications of the Aadhaar system, particularly regarding the misuse of personal data and the agency's authority over legal actions related to violations.
- Concerns are raised about the Aadhaar Act, which limits individuals' ability to sue for misuse of their Aadhaar information.}
- A report reveals that 130 million Aadhaar numbers were leaked, prompting questions about the potential dangers of such data exposure.}
- The legality of integrating Aadhaar numbers into various databases is questioned, highlighting that it may not be legally permissible.}
- The potential for database convergence raises alarms about centralized access to personal data by governmental authorities.}
- The implications of linking Aadhaar numbers to multiple databases are discussed, emphasizing the risks associated with data privacy.}
[22:41](
The discussion focuses on the implications of biometric data security and the effectiveness of Aadhaar in combating corruption, while also questioning the government's claims about financial savings from the system.
- Concerns are raised about the security of biometric data, with instances of hacking being reported.}
- The potential of Aadhaar to reduce corruption is debated, with opinions on its effectiveness in enforcing accountability.}
- The government claims significant savings due to Aadhaar implementation, but lacks detailed evidence to support these assertions.}
- The conversation touches on the widespread adoption of Aadhaar, with some participants indicating they do not possess an Aadhaar card.}
[26:30](
The discussion highlights the transformative potential of Aadhaar as a biometric identification system, comparing its impact on society to that of app stores in the tech industry. It emphasizes the accessibility it provides to various sectors and the direct benefits to the population, especially the economically disadvantaged, while acknowledging the need for ongoing debates about its implementation and privacy concerns.
- The speaker expresses admiration for Aadhaar, noting its uniqueness in the global context.}
- Aadhaar is likened to the app revolution, suggesting it has the potential to significantly change lives by providing an open system for various industries.}
- The system's impact is highlighted as it benefits not only the affluent but also the economically disadvantaged, ensuring subsidies reach the intended recipients.}
- Concerns regarding data privacy and the legal framework are raised, but there's a strong argument against dismantling the system entirely.}
The documentary explores China's advanced surveillance systems, social credit scoring, and data collection practices, raising questions about privacy, ethical concerns, and global implications.
Detailed Summary for [China - Surveillance state or way of the future? | DW Documentary](
by [Monica](https://monica.im)
[00:02](
The video explores the pervasive surveillance technology in China, highlighting the impact of modern tech on daily life and privacy concerns.
- Introduction to the extensive surveillance system in Shanghai, where residents are constantly monitored by cameras.}
- Discussion on the implications of Chinese technology on global data privacy and control over personal information.}
- A family's embrace of modern technology, including the use of smart devices for communication and entertainment.}
- Description of Hangzhou as a rapidly growing high-tech metropolis, showcasing the integration of technology in urban living.}
[05:16](
The video discusses China's extensive surveillance system, detailing how it monitors residents in real-time and aims for complete coverage across public spaces to maintain social stability.
- Introduction of a surveillance system that allows real-time monitoring of residents and their activities.}
- The Chinese government's overarching plan for surveillance aims for complete coverage in major public areas, showcasing the speed of police identification.}
- Researcher Mariko Ulberg tracks China's growing security measures, highlighting the detailed data collected on surveillance schemes.}
- The rationale behind monitoring citizens is to prevent social conflict, which could threaten the government's stability.}
[10:35](
The video discusses how TikTok's algorithm works to keep users engaged by collecting personal data and tailoring content to individual preferences, highlighting the implications of such surveillance.
- The algorithm is designed to keep users scrolling by tracking their preferences and continuously offering tailored content.}
- Researchers analyze TikTok to reveal what kind of personal data is being collected from users.}
- The video showcases real-time data transmission from TikTok, illustrating how it collects information like location and user interactions.}
- TikTok's algorithm improves over time by using collected data to enhance personalized recommendations, making it more effective than other social media platforms.}
[15:57](
The video segment explores the implications of surveillance and data collection in China, particularly in the context of public health measures during the COVID-19 pandemic. It highlights the experiences of an artist and the contrasting approaches to data privacy in China and Germany.
- The artist documents a group of volunteers walking under surveillance cameras in Beijing, emphasizing the choreographed nature of their movements.}
- The artist expresses frustration over censorship and the inability to share his work, which critiques privacy concerns not only in China but globally.}
- Health authorities in China utilize apps to track individuals' health status and potential COVID-19 exposure, demonstrating the intersection of technology and public health.}
- Researchers compare China's health app with Germany's, highlighting significant differences in data protection and privacy laws between the two countries.}
- The analysis reveals that the Chinese app collects and transmits location data, raising concerns about surveillance and individual privacy.}
[21:13](
This section discusses China's extensive data collection practices and the implementation of a social credit system that incentivizes positive behavior while penalizing rule violations.
- China is a leader in personal data collection, with both government and companies involved.}
- The social credit system rewards individuals for good behavior and penalizes those who violate laws or regulations.}
- The transparency of what data is collected and how scores are calculated remains unclear.}
- Authorities use a combination of rewards and punishments to encourage compliance among citizens.}
- The system aims to enforce laws more effectively by linking compliance to potential future benefits.}
[26:37](
The video explores the growing presence of Xiaomi in Germany, highlighting its innovative products and the challenges it faces regarding data privacy and consumer trust.
- Xiaomi's headquarters in Düsseldorf is focused on integrating its products into daily life and capturing the German market.}
- Despite promising innovation at low prices, Xiaomi faced a scandal regarding user data privacy that raised concerns among German consumers.}
- Research revealed that Xiaomi phones were transmitting personal user data, leading to accusations of surveillance, which the company later denied.}
- Data protection is highly valued in Germany, contrasting with the more transparent consumer environment in China, where government surveillance is prevalent.}
[31:49](
The video discusses the implications of surveillance technology in China, particularly in Xinjiang, highlighting the tension between technological advancement and privacy concerns.
- A tech expert expresses fascination with technology but raises concerns about privacy invasion due to pervasive surveillance.}
- The rapid adoption of surveillance in Xinjiang is examined, showcasing the state's control over the predominantly Muslim Uighur population.}
- A personal account from a Uighur woman living in the Netherlands contrasts the freedom of expression in her current life with the oppressive surveillance in her homeland.}
- The extensive network of surveillance cameras in Urumqi illustrates the Chinese government's capability to monitor its citizens continuously.}
[37:08](
This section of the documentary delves into the harsh realities of the Chinese government's treatment of the Uyghur population, focusing on the existence of internment camps and the use of advanced surveillance technology to monitor and control this minority group.
- The narrator realizes they have been taken to a prison camp, not a school, highlighting the deceptive nature of such facilities.}
- The Chinese government denies the existence of these camps, referring to them as vocational training centers, while international observers report significant human rights abuses.}
- Reports of torture and violence within the camps are discussed, including a tragic incident involving a young woman who died due to lack of medical care.}
- The documentary shifts focus to technology companies analyzing surveillance equipment, revealing alarming features that categorize individuals based on their race.}
- A specific surveillance system is designed to alert police about individuals from the Uyghur minority, showcasing the financial incentives driving such oppressive measures.}
Eric Schmidt's candid talk at Stanford reveals his controversial views on AI, remote work, and tech oligarchy, exposing a detached mindset prioritizing profit over ethics, regulation, and societal impact.
Former Chinese leader Jiang Zemin passionately addresses reporters, criticizing their questions as "too simple, sometimes naive," emphasizing media's need for knowledge and responsibility while sharing his experiences.
Nicolae Ceaușescu's final speech showcases his attempt to address a restless crowd, emphasizing unity and sovereignty, but chaos unfolds as the audience grows increasingly agitated.
Nietzsche's philosophy, rooted in Darwinism and rejecting morality and religion, is critiqued by Chesterton as despairing, aristocratic, and ironically self-contradictory.
A young man confronts corporate greed as a ruthless mentor defends capitalism, wealth disparity, and the illusion of democracy in a high-stakes financial world.