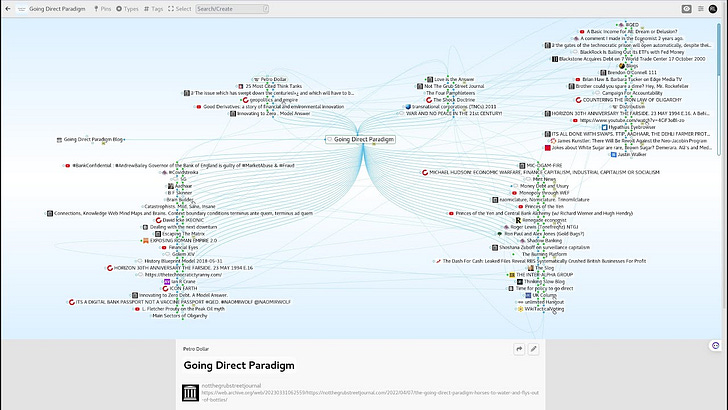
Affordable Housing, Show me an Angle and I’ll show you an edge. #MOAB #QED
ChatGPT.And Climate Alarmism. And they call it Artificial Intelligence!
QED Post Climate Change, Land Use and Monetary Policy, The New Trifecta.
Doubling Back I often find it somewhat more productive than doubling down. Doubling Down is a form of denial and Doubling Back is a retracing of steps to find where one took a misstep. Whilst the end of the World is not nigh, the end of the current monetary arrangements is nigh, and also the old social contract is up in flames and withering away as I type…
34:51
Blog about four years ago saying you know was it
sh Show me a what was it it was quite a catchy line I can't remember something
was it show me an honest billionaire was it that one ?
no no it was it
Affordable Housing, Show me an Angle and I’ll show you an edge. #MOAB #QED
AUTHOR:ROGERGLEWIS PUBLISHED DATE:JUNE 18, 2022
Give them what they want.
certain patterns were universal. Semis sold better than terraces. Houses sold better than flats – at first by almost 50 to one. Low-rise flats sold better than high-rise ones. Properties with gardens or garages were strongly in demand. Rural and suburban properties sold better than urban ones. Homes on small estates sold better than homes on large ones. Homes with non-council neighbours were the most sought after of all.
Similar subtle and not so subtle social gradations defined the buyers. A thorough, politically neutral national survey conducted by the Department of the Environment in 1985–6 and published in 1988, looking back at the first five years of the right to buy, found that: “[Purchasers] were a highly diverse group but … clearly not representative of [council] tenants as a whole. Buyers were disproportionately drawn from the middle-aged and the better-off, many with adult children sharing the home and the expenses. Most were in full-time work, usually manual skilled or white-collar occupations, and with more than one wage-earner in the household. Buyer incomes were on average about double tenant incomes.”
https://www.theguardian.com/society/2015/aug/26/right-to-buy-margaret-thatcher-david-cameron-housing-crisis
1979 Conservative Manifesto.
5. Helping the family
HOMES OF OUR OWN
To most people ownership means first and foremost a home of their own.
Many find it difficult today to raise the deposit for a mortgage. Our tax cuts will help them. We shall encourage shared purchase schemes which will enable people to buy a house or fiat on mortgage, on the basis initially of a part-payment which they complete later when their incomes are high enough. We should like in time to improve on existing legislation with a realistic grants scheme to assist first-time buyers of cheaper homes. As it costs about three times as much to subsidise a new council house as it does to give tax relief to a home buyer, there could well be a substantial saving to the tax and ratepayer.
The prospect of very high mortgage interest rates deters some people from buying their homes and the reality can cause acute difficulties to those who have done so. Mortgage rates have risen steeply because of the Government’s financial mismanagement. Our plans for cutting government spending and borrowing will lower them.
THE SALE OF COUNCIL HOUSES
Many families who live on council estates and in new towns would like to buy their own homes but either cannot afford to or are prevented by the local authority or the Labour government. The time has come to end these restrictions. In the first session of the next Parliament we shall therefore give council and new town tenants the legal right to buy their homes, while recognising the special circumstances of rural areas and sheltered housing for the elderly. Subject to safeguards over resale, the terms we propose would allow a discount on market values reflecting the fact that council tenants effectively have security of tenure. Our discounts will range from 33 per cent after three years, rising with length of tenancy to a maximum of 50 per cent after twenty years. We shall also ensure that 100 per cent mortgages are available for the purchase of council and new town houses. We shall introduce a right for these tenants to obtain limited term options on their homes so that they know in advance the price at which they can buy, while they save the money to do so.
As far as possible, we will extend these rights to housing association tenants. At the very least, we shall give these associations the power to sell to their tenants.
Those council house tenants who do not wish to buy their homes will be given new rights and responsibilities under our Tenants’ Charter.
REVIVING THE PRIVATE RENTED SECTOR
As well as giving new impetus to the movement towards home ownership, we must make better use of our existing stock of houses. Between 1973 and 1977 no fewer than 400,000 dwellings were withdrawn from private rental. There are now hundreds of thousands of empty properties in Britain which are not let because the owners are deterred by legislation. We intend to introduce a new system of shorthold tenure which will allow short fixed-term lettings of these properties free of the most discouraging conditions of the present law. This provision will not, of course, affect the position of existing tenants. There should also be more flexible arrangements covering accommodation for students. At the same time, we must try to achieve a greater take-up in rent allowances for poorer tenants.
https://web.archive.org/web/20130522104806/http://www.politicsresources.net/area/uk/man/con79.htm#sale
Home ownership in England at a 30-year low, official figures show
English Housing Survey finds private rented sector doubled in size since 2004, with ownership at lowest level since 1985
https://www.theguardian.com/money/2017/mar/02/home-ownership-in-england-at-a-30-year-low-official-figures-show
Thatcher’s legacy: A shortage of affordable housing
Meanwhile, owners of ex-council flats continue to reap big profits. Many of the tenants sold their properties to investors or property companies, which were able to jack up the rents in a tight market. Last month, the Daily Mirror reported that Charles Gow, the son of Mrs. Thatcher’s housing minister, Ian Gow, bought 40 of the 120 former council flats in one housing project in Roehampton, in South West London. Rents for the former council flats have soared, leaving some low-income tenants begging for higher rental subsidies. “Speculators have made millions out of exploiting public assets,” Tony Belton, a Labour councillor in South West London, told the Mirror. “It stinks.”
Prof. Tunstall said that neither the government of Prime Minister David Cameron nor the local authorities have any credible solution to the low-cost housing shortage, and the shortage is getting worse. “It’s one of the top policy issues here,” she said. “We’re only getting a trickle of new housing.”
ERIC REGULYEUROPEAN BUREAU CHIEF
LONDON
Thatcher helped people to buy their own homes – but the poorest paid the price
November 27, 2015 3.17pm GMT
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Housing_Act_1980
Opponents have also claimed that the Right to Buy Scheme has contributed to the decline in the stock of affordable housing. The UK is widely regarded as having a poor record in building new low cost housing for much of the period between 1960 and 2020. In the face of a booming property market, many not eligible for the Right to Buy have found themselves completely unable to do so.
Despite the stated ambition post 2015, to replace right to buy sales, with new replacement housing stock, there is concern that this is not happening in practice. Government statistics in January 2021, revealed that for a total of 41,541 additional Right to Buy sales, which should have been replaced by the end of September 2020 in line the Government’s three-year replacement policy, only 31,661 replacement starts and acquisitions have occurred, leaving a replacement shortfall of 9,980 homes.
Quotes
“It cannot be right that not only are we not building enough homes for social rent, we are losing them at a time when we need them more than ever. Our analysis shows that we have lost more than 150,000 social rented homes between 2012 and 2017 due to right to buy and other factors, and that figure will reach 230,000 by 2020 unless we take action now”…”We support the principle of helping tenants move into home ownership but it cannot be at the expense of other people in need. We need to look at fairer ways to help tenants into home ownership, because this is clearly not the way to do it.” – Terrie Alafat , Chief Executive, Chartered Institute of Housing, 2018.
In an email to employees last week, Katerra CEO Michael Marks had a few uplifting thoughts on the year gone by.
His startup, which seeks to transform the $12 trillion global construction industry through technology and automation, has grown to more than 8,000 employees, is nearing profitability and will soon open a new state-of-the-art factory in California. Clients are returning, he wrote, and the company has more than $15 billion worth of building projects in a pipeline spanning the United States to Saudi Arabia.
“We can say with pride,” Marks wrote of the company’s feats, “that once we begin a project, we never walk away from that job.”
But his message glossed over a few key facts. In the last month, Katerra’s co-founder quietly left the firm’s board, the company closed its first factory and hundreds of employees have been laid off.
And the firm’s patchy track record of delivering projects stands in stark contrast to Marks’ assertion. In fact, The Real Deal found, Katerra has failed to complete roughly a dozen projects and could only name one that was delivered on time (the company says 26 prefab projects will be delivered by the close of 2019). All the while, logistical and technology-based issues have chipped away at the company’s image as a revolutionary tech startup.
Michael Marks, CEO of Katerra
Some clients have ended their relationship with the firm. Other clients, however, are tied to Katerra’s executives, and have drummed up business for the company — a similar arrangement used by WeWork executives, which became a concern for some investors when the co-working firm planned to go public.
Despite the turbulence, Katerra continues to grow rapidly in the U.S., having acquired at least eight general contractors and architecture firms in the past two years and more than 20 companies total since its founding.
“Katerra is nothing but a developer on steroids,” said one former employee, who was among more than a dozen people interviewed for this article that worked with, or for, Katerra. Many signed non-disclosure agreements and did not want to be identified.
Katerra’s largest investor, SoftBank, has played a major role in driving its valuation north of $4 billion, and has poured more than $1 billion into the company. Other major investors such as Foxconn and DFJ have signed on, while executives from Google, Amazon and Electronic Arts have joined the company’s leadership.
According to Katerra, the company has raised more than $2 billion from investors, including a recent $700 million funding round led by SoftBank. Though multiple news organizations reported that the funding was pending, Katerra never publicly announced its completion, an unusual move for a company that is able to command capital of that size. (That infusion did not appear in public filings, a company spokesperson said, because it was part of a private placement. Filings with the Securities and Exchange Commission show that Katerra raised a little more than $2 billion by the end of 2018.)
With this kind of hype, the Silicon Valley company’s rise follows a similar narrative to that of other SoftBank-backed startups, including WeWork, Compass and Uber: Break down the walls of an industry, grow at all costs and figure out the metrics later.
“Think of any startup in the last 20 years. Katerra has grown faster than most and got to unicorn status,” said Mark Randall, Katerra’s first CEO. “So I think there’s a cleanup happening.”
As the company has sought to bolster its reputation in the U.S., Katerra has inked massive deals overseas, in Saudi Arabia and India, where it has committed to building hundreds of thousands of homes. In an email to employees, Marks said the Saudi Arabia deal is valued at $40 billion.
“While we have realigned resources in our company this year, overall Katerra has grown,” Katerra spokesperson JZ Rigney said in a statement.
Rigney also clarified Marks’ email to employees sent last week to say that the company takes pride in completing its jobs “once construction begins.”
Executive fractures
Over three decades, Marks has worked his way to the top ranks of Silicon Valley’s elite. In the 1990s, he steered electronic components manufacturer Flextronics from the brink of bankruptcy, went on to briefly lead Tesla as CEO and served on GoPro’s board of directors.
Fritz Wolff
“He’s a pretty amazing deals guy, and the respect for Michael in Silicon Valley is off the charts,” said Randall, who said he left Katerra on good terms to return to consumer electronics.
In forming Katerra in 2015, Marks’ friend and longtime business partner, Fritz Wolff, suggested they create a Flextronics for construction — effectively a vertically integrated company that controlled the entire building process; instead of hiring an architect, an engineering firm, a general contractor and subcontractors, Katerra could do it all.
To do this, Marks’ tapped his relationships in Silicon Valley to launch a web of companies that propped up Katerra, some serving as its investors, others as customers, or sometimes both, TRD has learned. The arrangement is reminiscent of ownership structures at WeWork, where its former CEO Adam Neumann personally owned buildings that he leased back to his company — a friction point for investors ahead of its failed public offering.
For example, Wolff, who joined Katerra as co-founder, owns a private equity firm with a massive construction arm that was Katerra’s sole customer in its initial years, providing it with more than a dozen projects.
In addition to Marks and Wolff, renowned tech investor James Davidson also joined Katerra as a co-founder. Together, the three launched a separate firm known as Paxion Capital, which they used to invest in other Katerra customers.
James Davidson of Silver Lake
Through Paxion, the trio invested in candy store retailer, Lolli & Pops. The retailer, which filed for bankruptcy in August, lists Katerra as one of its creditors, with $2.9 million owed for renovation work. (Paxion’s CFO Duncan Roberts, who at one time served as Katerra’s CFO, is listed as a member of Lolli & Pops’ board of directors.)
“With a group of people, who are also the customers, that’s where a potential conflict of interest emerges,” said Richard Morris, a partner at Allegaert Berger & Vogel, who specializes in securities law. “That’s a question of how it’s disclosed and dealt with.”
A Katerra representative said in a statement that it “values good corporate governance and has policies and procedures that align with public company reporting standards.”
The co-founders also launched an investment fund called Kandle, which in part allowed them to take an equity position in some of Katerra’s projects. While it’s not clear exactly how much Kandle has raised, internal documents seen by TRD show that Katerra has forecasted that the fund’s capital could nearly double Katerra’s development starts to $2.1 billion by 2022.
Last month, however, fractures began to appear in Katerra’s leadership after Wolff quietly left the company’s board. People who have spoken with Wolff since his departure described the split as acrimonious, and it has raised questions about the potential impact on Katerra’s portfolio.
According to Katerra, Wolff left to “concentrate on other professional pursuits,” but remains a shareholder and supporter of the company. Both Wolff and Katerra maintain that they will continue working together. In an email to employees last week, Marks said that Wolff represents only 15 percent of Katerra’s customer base.
“Katerra has continued to improve its processes since launching, and we continue to support their vision,” a spokesperson for the Wolff Company said in an email. “We currently have 17 projects under construction with Katerra and continue to assess new opportunities to work together.”
Tech trials
Katerra has said its mission is to deliver construction projects that are “better, faster and cheaper.” Through tech, the company says, it can streamline the antiquated processes that plague the construction industry.
Such claims are a hallmark of a generation of startups that aim to disrupt their respective industries by replacing byzantine systems with tech. Katerra says it has applied for almost 60 patents, the bulk of which have been filed in the past 18 months. A handful of those have been approved, though they relate to electrical systems and mass timber production.
But like other firms in the SoftBank portfolio, Katerra has faced questions about whether its tech-enabled business model is deserving of the firm’s massive valuation.
Its decision to close the Phoenix factory suggests a failed attempt to achieve this goal. When it opened in 2017 as the company’s first facility, its primary purpose was to manufacture prefabricated components — including wall and floor panels — that could be shipped to construction projects. A series of high-tech machines would assemble the components, which were tracked with an RFID chip system.
But soon enough, problems surfaced with some materials made in Phoenix. At its first project in Spokane, Washington, known as Riverhouse, wall panels made of timber arrived at the job site warped and unusable, according to two people familiar with the matter. One person involved in the project said this was because the timber, sourced from the wet climate of Washington, was trucked to Phoenix, where it sat in searing heat, and became warped.
“No one understood from the beginning why we had the Phoenix factory,” said one former employee.
Steve Weilbach, Katerra’s head of sales, said the Phoenix factory’s closure was merely a result of the company opening a “newer more advanced” facility in California.
Following the announcement that more than 200 employees would be laid off as a result of the closure, Marks vaguely acknowledged the shortcomings of the Phoenix factory in an email to employees: “We learned what we were doing right, and we also learned about lots of improvements that could be made.”
“Key customers”
Katerra’s roster of Silicon Valley stars and its pairing with the Wolff company has been an effective way to attract business. In a 2018 presentation, investor Navitas Capital noted that Katerra was bolstered by a multifamily pipeline handed over from Wolff, which enabled the company to “act on the initial inertia to attract key customers.”
But some of these “key customers” have since ended their relationship with Katerra. The Sobrato Organization, which was working with Katerra on a project in Sunnyvale, California, consisting of 135 townhouse units, confirmed to TRD that they are no longer working with the company. The project, at 1139 Karlstad Drive, had been dogged by disagreements over costs, The Information previously reported.
Another issue that has caused friction among clients are cost overruns. One problem, former employees say, was a flawed process the company used to price jobs. In addition to estimating the price of a job, Katerra would apply a discount to prove that it could deliver its projects cheaper than conventional construction companies.
At one project it developed with Wolff’s firm, a 554-unit residential site in Kirkland, Washington, known as Lifebridge, Katerra’s estimators priced the job at close to $90 million in 2017. According to a former employee who raised concerns with Katerra executives about the pricing, the warning fell on deaf ears. Instead, Katerra executives later expressed shock after learning that the job would actually cost closer to $140 million — almost $50 million more than it had agreed to.
Weilbach, Katerra’s head of sales, said that in the case of Katerra’s earliest customers, including Wolff, the company often took over projects after much of the design work was already completed. Since Katerra wasn’t controlling all aspects of such projects, the company’s touted cost and time efficiencies weren’t always realized.
“It’s much harder for us to apply that value when we take over someone else’s work versus starting from inception,” Weilbach said.
Some projects have been abandoned altogether. Internal documents obtained by TRD show that of 57 projects Katerra was overseeing in the U.S. at the end of January 2019, nearly a dozen appear to be dead or have halted. (The company said its pipeline, currently at 300-plus projects, includes those overseen by firms it has acquired. That figure also includes jobs in which it worked in various capacities – performed engineering work or provided other services, for example – but was not the general contractor.)
One of those projects was a 120-room hotel in California known as Tru by Hilton. In 2018, Katerra was hired by California-based RAR Hospitality to handle construction management and design of the hotel. The hotel would be Katerra’s first, and its executives expressed enthusiasm to RAR leaders that the project would help launch the company into the hospitality space.
But a month before construction was slated to begin, Katerra backed out.
“They touted us as one of the most important projects in the company,” said Cameron Lamming, an executive at RAR. “And then dumped us.”
A $40 billion question
While some of the company’s U.S. projects have run into issues, Katerra has turned its attention to even more ambitious projects in Saudi Arabia and India. The company’s operations there, in some ways, mirror its strategy in the U.S: Grow quickly through acquisitions and build factories to accommodate an influx of work.
“They got a bucket full of money. The question is whether the market is ready for them.” — Rich Wood, chairman and CEO of Plaza Construction
In Saudi Arabia, Katerra won a competition last year after building a 1,334-square-foot home in 48 hours. As a reward, the firm inked a non-binding agreement to build hundreds of thousands of housing units in Saudi Arabia, with the first phase being 4,101 homes.
The connection is unsurprising: Saudi Arabia is the largest backer of SoftBank’s Vision Fund — the vehicle backing Katerra.
“We help our portfolio companies navigate entrance to new and promising markets, such as Katerra’s work for Saudi Arabia,” a SoftBank spokesperson said in a statement.
If executed, Katerra’s plans would reshape the country. In his email to staff last week, Marks said that the agreement with Saudi Arabia is valued at $40 billion — almost twice the cost of Hudson Yards in New York.
To start, Katerra says it will be building 10 to 15 homes a day by the second quarter of 2020. A representative said the company has broken ground on one factory in Saudi Arabia and has plans for another.
Further east, the company has also unveiled plans for a massive operation in India. In June 2018, it announced its acquisition of India-based KEF Infra., a four-year-old infrastructure manufacturer. According to news reports at the time, the venture had $3.7 billion worth of work booked across India and North America.
KEF Infra’s Faizal Kottikollon and Katerra’s Michael Marks (Image via India CSR Network)
“They got a bucket full of money,” said Rich Wood, chairman and CEO of Plaza Construction. “The question is whether the market is ready for them.”
A second-generation factory
Back in the U.S., Katerra hailed the closure of its Phoenix factory as part of the company’s next phase. In a blog post, Katerra described the factory as its “first-generation approach to building component manufacturing,” which it has advanced significantly in a new factory it’s building in Tracy, California.
According to Katerra, construction on the Tracy facility is nearly complete, and is expected to produce some 12,500 multifamily units on an annual basis — or three times as much as the Phoenix factory.
A year ago, the company told California officials that its business model relied on construction sites being within 500 miles of the new factory. At the time, Katerra said it had 17 projects underway in the area, though the status of these projects is unclear. A spokesperson for the company noted that the factory is near rail, shipping ports and freeways, which will enable transport in the region.
However, at least three major multifamily projects in that radius have since stalled or been abandoned, including the Sobrato development in Sunnyvale. Tracy’s City Council approved a 264-unit project on Valpico Road, but construction hasn’t started. Katerra says construction is slated to begin in the spring.
“They were supposed to start construction in November,” said Tracy Planning Commissioner Joe Orcutt, who voted against the project. “We’ve all been kind of waiting.”
Correction: An earlier version of this story misidentified which of RAR Hospitality’s projects Katerra worked on. It was Tru by Hilton.
Contact Kathryn Brenzel at kathryn@therealdeal.com and David Jeans at dj@therealdeal.com.
Housing Collapse Coming Right Up
Mortgage rates are high and rising. Refinancing opportunities are nonexistent; home affordability has collapsed.
MISHMAR 5, 2018 go to wayback link in title for rest of post.
ChatGPT.And Climate Alarmism.
Q? Is Climate Alarmism not even wrong.?
“Climate alarmism” is a term that is often used by those who believe that concerns about climate change are exaggerated or misplaced. However, the overwhelming majority of scientists who study the issue believe that climate change is real, caused by human activity, and poses a significant threat to the planet. The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), which is a body of scientists from around the world established by the United Nations, states that it is “extremely likely” (95-100% probability) that human activities, particularly the burning of fossil fuels, are the dominant cause of global warming since the mid-20th century. The impacts of climate change, such as sea level rise, more frequent and severe heatwaves, and more intense storms, are already being observed. Therefore it is not accurate to say that climate alarmism is not even wrong
Q?. Dr. Roy Spencer and Dr Judith Curry's UAI satellite record and Climate etc challenge the AGM co2 sensitivity as well as the accuracy of modeled temperature anomalies. The number of supporters of the AGM hypothesis comes from a non-scientific source and many IPCC authors have withdrawn support for the narrative around their work. It seems disputable to say Climate Alarmism is not even wrong. Indeed Alarmism seems pseudo-scientific and religious in nature not objective and empirical.?
While it is true that there are some scientists who have raised questions about certain aspects of the mainstream scientific understanding of climate change, the overwhelming majority of scientists who study the issue believe that climate change is real, caused by human activity, and poses a significant threat to the planet. The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), which is a body of scientists from around the world established by the United Nations, states that it is “extremely likely” (95-100% probability) that human activities, particularly the burning of fossil fuels, are the dominant cause of global warming since the mid-20th century. The IPCC is a consensus-based organization, whose reports are based on the work of thousands of scientists from around the world, and its conclusions are supported by multiple lines of evidence.
It is also worth noting that there are some scientists and organizations that have been criticized for their association with groups that are funded by the fossil fuel industry or have ties to conservative think tanks. These individuals and groups have been accused of spreading misinformation about climate change and working to undermine public trust in the scientific consensus on the issue.
It is important to remember that scientific understanding is a dynamic process, and new research and data may lead to revisions or updates to the current understanding of certain aspects of climate change. However, the overall scientific consensus on the reality and causes of climate change remains robust and supported by a large body of evidence.
In summary, while there are some dissenting voices on certain aspects of the mainstream scientific understanding of climate change, the overwhelming majority of scientists who study the issue believe that climate change is real, caused by human activity, and poses a significant threat to the planet. Therefore, it is not accurate to say that climate change alarmism is not even wrong
Q?. Is the main focus of Carbon rationing financial rather than environmental in motivation Clive Spash’s paper on The Brave New World of carbon trading seems relevant still to this question as well as Sandors work
Carbon rationing, also known as carbon pricing or carbon trading, is a policy approach that aims to put a price on carbon emissions in order to reduce them. The idea is that by putting a price on emissions, companies and individuals will have an economic incentive to reduce their emissions, as it will be more expensive to emit more carbon.
Some critics have argued that the main focus of carbon rationing is financial, rather than environmental in motivation. They argue that carbon trading is primarily driven by the desire to create new financial markets and generate profits for banks and other financial institutions, rather than being motivated by a genuine desire to address climate change.
The work of Clive Spash, a researcher in environmental policy, has been critical of carbon trading, arguing that it is primarily a way for governments and corporations to avoid taking more direct and effective actions to reduce emissions. He has also argued that carbon trading could lead to the creation of a new form of colonialism, in which the developed world continues to emit greenhouse gases while buying carbon credits from developing countries.
Sandor’s work also criticized carbon rationing as a financial mechanism rather than a real solution to the problem of climate change, and pointed out that it could lead to manipulation of the markets, lack of transparency, and other issues.
It is important to note that Carbon rationing is one of the policy approach to mitigate the climate change and it is not the only one. The effectiveness of carbon pricing mechanisms depends on how they are designed and implemented, and different policy approaches may be more or less effective in different contexts.
In conclusion, while carbon rationing can be a valuable tool for reducing carbon emissions, it is important to recognize that it is not a silver bullet for addressing climate change. Critics argue that the main focus of carbon rationing is financial, rather than environmental in motivation, and that it may not be the most effective way to address the problem
Q?.Dyson Freeman disputed the notion of global temperature measurement and Claes Jonson dispute the mathematics of the CO2 warming effects,
It is true that there are some scientists and researchers who have raised questions about certain aspects of the mainstream scientific understanding of climate change, including the measurement of global temperatures and the mathematical models used to estimate the warming effects of CO2.
Dyson Freeman, a theoretical physicist and mathematician, has disputed the notion of global temperature measurement, arguing that the temperature records used to estimate global warming are unreliable and that the warming trend is not as significant as commonly believed.
Claes Johnson, a mathematician and engineer, has also disputed the mathematics used in climate models to estimate the warming effects of CO2, arguing that the models exaggerate the warming effect and that the actual warming from a doubling of CO2 is likely to be much less than the models predict.
It’s worth noting that while some scientists have raised questions about certain aspects of the mainstream scientific understanding of climate change, the overwhelming majority of scientists who study the issue believe that climate change is real, caused by human activity, and poses a significant threat to the planet. The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), which is a body of scientists from around the world established by the United Nations, states that it is “extremely likely” (95-100% probability) that human activities, particularly the burning of fossil fuels, are the dominant cause of global warming since the mid-20th century. The IPCC’s conclusions are based on the work of thousands of scientists from around the world, and are supported by multiple lines of evidence.
It is important to keep in mind that scientific understanding is a dynamic process, and new research and data may lead to revisions or updates to current understanding of certain aspects of climate change. However, the overall scientific consensus on the reality and causes of climate change remains robust and supported by a large body of evidence
Q?.Belief in the scientific method would suggest that what is provable empirically is what counts climate models fail to model the past they have been falsified how then can they form the basis for policymaking when they have been at best crude based upon their results?
The scientific method is based on the idea that scientific knowledge is acquired through observation and experimentation and that theories and hypotheses must be tested and supported by evidence in order to be considered valid. Climate models are a tool used by scientists to simulate and predict the Earth’s climate system, and are based on a set of assumptions and equations that describe the physical processes that govern the climate.
It is true that climate models have some limitations, and that they are not perfect representations of the real world. There are uncertainties associated with the input data and the model parameters, and the models may not fully capture all of the processes that influence the climate. Additionally, climate models are only able to simulate the past climate to a certain degree of accuracy, and small differences between the modeled and observed climate can occur.
However, it is important to note that despite these limitations, climate models have been able to accurately simulate and predict many aspects of the climate, such as global warming, sea level rise, and changes in precipitation patterns. The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) periodically assesses the performance of climate models and concludes that climate models have been successful in simulating the past and present climate and in providing projections of future climate change.
Moreover, the models are constantly being updated and improved, and new observational data is continually being incorporated into the models to improve their accuracy. The use of multiple models and different scenarios allows scientists to estimate the range of possible future outcomes and take into account the uncertainties associated with the models.
In summary, while climate models have limitations and are not perfect representations of the real world, they are still valuable tools for simulating and predicting the Earth’s climate system. They have been successful in simulating the past and present climate and in providing projections of future climate change. They are constantly being improved and updated, and new observational data is continually being incorporated into the models to improve their accuracy. Therefore, climate models still provide a solid basis for policy making
Q?: Claiming that Climate models have been accurate requires proof, Manns Hockey Stick and Hansons original data has been found wanting and The UAE hiding the decline scandals all point to a failure to have repeatable results from the models this tends to refute any claims you are making about the IPCC and its claim to model efficacy.
It is true that some criticisms have been raised about certain aspects of climate modeling and the data used to support the mainstream scientific understanding of climate change.
One example is the “hockey stick” graph, first published by Michael Mann in 1998, which depicted a sharp increase in Northern Hemisphere temperatures in the 20th century and was widely cited as evidence for human-caused global warming. Some critics have argued that the hockey stick is based on flawed data and methods and does not accurately represent the historical temperature record.
Another example is the “hide the decline” scandal, in which emails from climate scientists were leaked and some scientists were accused of manipulating data and hiding information that didn’t support the idea of human-caused global warming.
It’s also worth noting that climate models are complex and require many assumptions and inputs, which can introduce uncertainties to the results. The models are also based on our current understanding of the physical processes that govern the climate, and as our understanding improves, the models will be updated accordingly.
It’s important to keep in mind, however, that despite these criticisms, the overall body of scientific evidence supporting the reality and causes of climate change remains robust. The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) regularly assesses the performance of climate models, and concludes that climate models have been successful in simulating the past and present climate and in providing projections of future climate change.
Additionally, many independent studies have confirmed the overall warming trend and the human influence on it. Furthermore, the scientific understanding of climate change is not based on a single study or a single set of data, but on a wide range of observational evidence, including temperature measurements, ice core records, and satellite data, as well as multiple lines of evidence from different sources.
In conclusion, while there have been some criticisms of certain aspects of climate modeling and the data used to support the mainstream scientific understanding of climate change, the overall body of scientific evidence supporting the reality and causes of climate change remains robust. The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) regularly assesses the performance of climate models, and concludes that climate models have been successful in simulating the past and present climate and in providing projections of future climate change
Q?.the claimed 97% consensus is false John Cooks's paper has been widely falsified
It is true that there has been some debate about the extent of scientific consensus on the reality and causes of climate change. One study, published in 2013 by John Cook and colleagues, surveyed 11,944 abstracts of scientific papers on climate change and found that 97% of the papers that took a position on the cause of recent global warming endorsed the view that it is primarily caused by human activity. However, this study has been criticized by some for the methodology used in determining the level of endorsement among the surveyed papers.
Another study conducted by the US National Academy of Sciences found that among actively publishing climate scientists, the consensus that humans are causing recent warming is over 90%. Also, numerous studies have been conducted in the past and most of them have reached similar conclusions.
It’s worth noting that while there is a broad scientific consensus on the reality and causes of climate change, it is important to keep in mind that scientific understanding is a dynamic process, and new research and data may lead to revisions or updates to current understanding of certain aspects of climate change.
In conclusion, while there has been some debate about the extent of scientific consensus on the reality and causes of climate change, the overwhelming majority of scientists who study the issue believe that climate change is real, caused by human activity, and poses a significant threat to the planet. Studies conducted in the past have found a high level of agreement among actively publishing climate scientists on the reality and causes of climate change
Q?.Are there parallels between the Nial Ferguson modeling of Covid and the Climate models both are wildly inaccurate and have a record of poor performance in thier predictions?
Both climate models and models used to predict the spread and impact of COVID-19 are complex mathematical tools that are used to simulate and predict the behavior of systems that are influenced by many factors. Both types of models have limitations and uncertainties associated with them, and there have been instances where predictions made by these models have not matched actual observations.
Climate models are based on a set of assumptions and equations that describe the physical processes that govern the climate. They are used to simulate and predict the Earth’s climate system and its response to various scenarios of greenhouse gas emissions. Climate models have been successful in simulating and predicting many aspects of the climate, such as global warming, sea level rise, and changes in precipitation patterns. However, they are not perfect representations of the real world and have some limitations, such as uncertainties associated with the input data and model parameters, and the models may not fully capture all of the processes that influence the climate.
Models used to predict the spread and impact of COVID-19 are based on a set of assumptions and equations that describe the transmission and progression of the virus. They are used to simulate and predict the spread of the virus and its impact on the population. These models have been used to inform public health policy and decision-making, but like climate models, they have limitations and uncertainties. Factors such as underreporting, asymptomatic carriers and changing behavior of people can make the predictions of these models less accurate.
It is worth noting that despite the limitations of these models, they can still provide valuable information and insight. Climate models and COVID-19 models are constantly being updated and improved with new data and research, and provide a way to explore and compare different scenarios.
In summary, both climate models and models used to predict the spread and impact of COVID-19 are complex mathematical tools that are used to simulate and predict the behavior of systems that are influenced by many factors, both of them have limitations and uncertainties, but they can still provide valuable information and insight.
And they call it Artificial Intelligence!